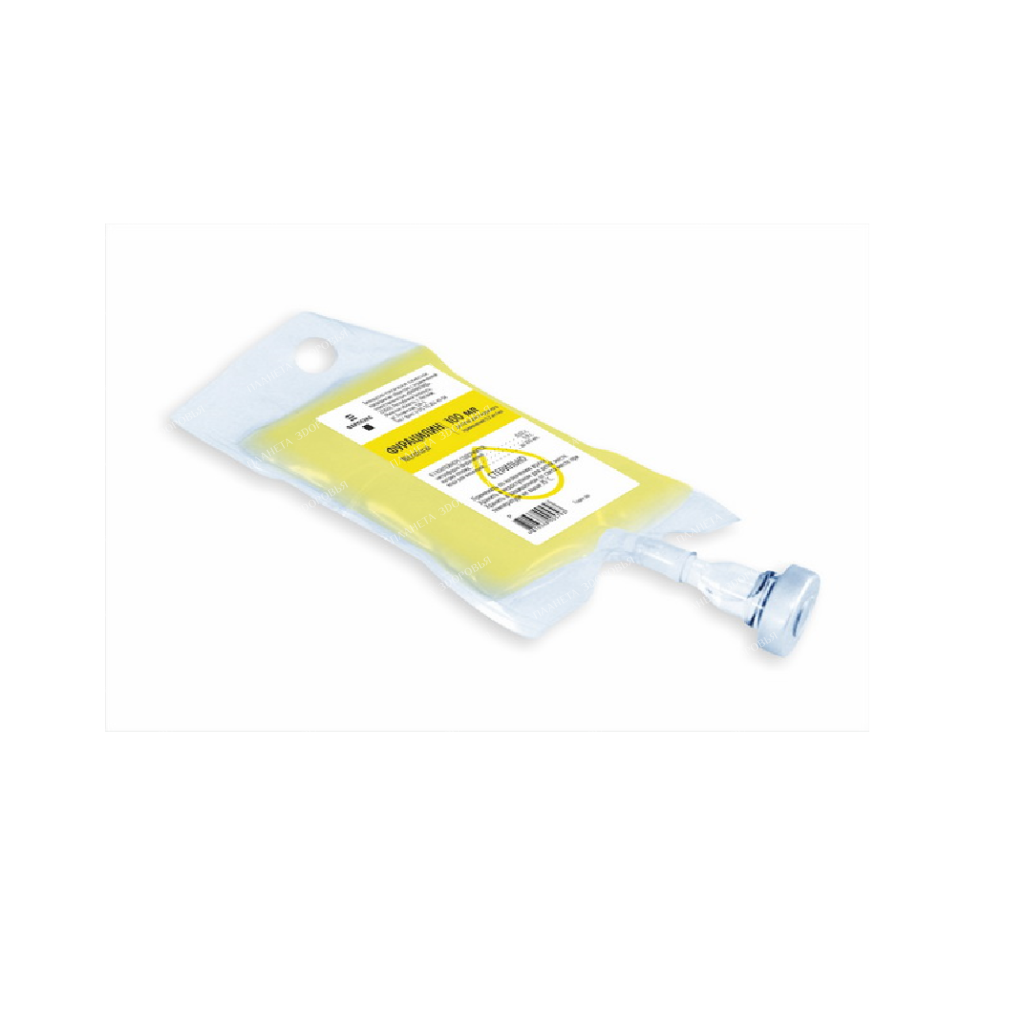
Furacilin solution for external use 0.2 mg/ml 100 ml №1
$9.00
Furacilin Solution for External Use: A Comprehensive Guide
Furacilin Solution for External Use 0.2 mg/ml 100 ml №1
is a powerful antiseptic solution used for a wide range of external infections and wounds. This comprehensive guide provides essential information about Furacilin, its uses, dosage, precautions, and potential side effects.
What is Furacilin Solution?
Furacilin solution is a topical antiseptic containing nitrofural, a potent antimicrobial agent effective against various bacteria and fungi. It is available as a 0.2 mg/ml solution in a 100 ml bottle.
Uses:
Furacilin solution is indicated for the treatment of a variety of external infections and wounds, including:
- Infected wounds: Cuts, abrasions, lacerations, and surgical wounds.
- Bedsore: Pressure ulcers and decubitus ulcers.
- Ulcers: Leg ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and other types of ulcers.
- Infected burns: Second and third-degree burns.
- Preparation for skin grafting: Preparation of the granulating surface for skin grafting.
- Osteomyelitis: Infections of the bone.
- Pleural empyema: Pus collection in the pleural cavity.
- Furuncle: Boils, particularly in the external auditory canal.
- Empyema of the paranasal sinuses: Pus collection in the sinuses.
- Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva (the transparent membrane that covers the white part of the eye).
Dosage and Administration:
The dosage and administration of Furacilin solution depend on the specific condition being treated.
- For purulent wounds, bedsores, ulcers, and burns: Irrigate the affected area with Furacilin solution and apply wet dressings.
- For osteomyelitis: Wash the cavity with Furacilin solution after surgery and apply a wet bandage.
- For pleural empyema: Drain the pus, wash the pleural cavity, and introduce 20-100 ml of Furacilin solution into the cavity.
- For furuncles and empyema of the paranasal sinuses: Wash the affected area 2-4-6 times a day, depending on the severity.
- For conjunctivitis: Instill 2-3 drops of Furacilin solution into the conjunctival sac 3-4 times a day.
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor, considering the disease’s characteristics, the patient’s tolerance to the drug, and the achieved effect.
Use During Pregnancy and Lactation:
When prescribing Furacilin solution to pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children, it is recommended to consider the potential risks and benefits of using this medication.
Precautions:
- Children and Adolescents: Furacilin solution is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 due to limited safety data.
- Cross-Sensitization: Prolonged use (more than 5 days) can lead to sensitization. If symptoms persist or worsen during use, discontinue use and consult a doctor.
- Drug Interactions: Furacilin solution is incompatible with epinephrine (adrenaline), tetracaine, procaine (novocaine), resorcinol, and other reducing agents. It is also incompatible with potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, and other oxidizing agents.
Side Effects:
Furacilin solution is generally well-tolerated when applied topically. Possible side effects include:
- Dermatitis: Skin inflammation requiring temporary suspension or discontinuation of the drug.
- Bleeding: Rarely, bleeding may occur at the application site.
Overdose:
Cases of overdose are rare when following the recommended usage instructions. Accidental ingestion may lead to nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness, and neuritis.
Contraindications:
- Kidney Function: Avoid using Furacilin solution if you have severe kidney problems.
- Allergic Dermatoses: Do not use if you have allergic skin conditions.
- Hypersensitivity: Do not use if you are allergic to nitrofuran derivatives.
Storage:
Store Furacilin solution in a cool, dark place at a temperature below 25°C. Keep out of reach of children.
Where to Buy:
Furacilin solution is available at most pharmacies. Please consult your doctor or pharmacist for the latest information on availability and pricing.
Disclaimer:
This information is provided for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Consult with your doctor or pharmacist for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Keywords:
Furacilin, Furacilin Solution, External Use, Antiseptic, Infected Wounds, Burns, Bedsore, Ulcers, Osteomyelitis, Pleural Empyema, Furuncle, Conjunctivitis, Dosage, Administration, Precautions, Side Effects, Overdose, Contraindications, Storage, Buy, Price, Treatment, Healthcare.
| INN | NITROFURAL |
|---|---|
| The code | 79 902 |
| Barcode | 4 810 368 005 793 |
| Dosage | 0.2mg/ml 100ml |
| Active substance | Nitrofural |
| Manufacturer | Pharmland SP LLC, RB, Belarus |
 Free worldwide shipping on orders $99+
Free worldwide shipping on orders $99+  US: temporary delays — postal services aligning new import rules,
US: temporary delays — postal services aligning new import rules,  EU: 1–2 weeks,
EU: 1–2 weeks,  Worldwide: 1–4 weeks
Worldwide: 1–4 weeks