-
×
 55mm Ashless Filter Papers, White Ribbon, 100 Count
1 × $9.00
55mm Ashless Filter Papers, White Ribbon, 100 Count
1 × $9.00 -
×
 Queen Pillow, 60x60cm: Luxurious Comfort
1 × $99.00
Queen Pillow, 60x60cm: Luxurious Comfort
1 × $99.00 -
×
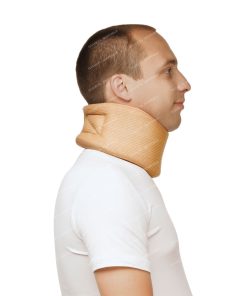 Bandage neck size 3
1 × $19.00
Bandage neck size 3
1 × $19.00 -
×
 Leather Orthotic Insoles with Arch Support: Comforma BALANCE Grand
1 × $79.00
Leather Orthotic Insoles with Arch Support: Comforma BALANCE Grand
1 × $79.00 -
×
 VEYLE ERGO Memory Foam Pillow: Anatomical Support (39x59x10cm)
1 × $79.00
VEYLE ERGO Memory Foam Pillow: Anatomical Support (39x59x10cm)
1 × $79.00 -
×
 White Crochet Mesh Hat
1 × $9.00
White Crochet Mesh Hat
1 × $9.00 -
×
 Olive Green Convertible Multi-Purpose Tote Bag SURT-01
1 × $109.00
Olive Green Convertible Multi-Purpose Tote Bag SURT-01
1 × $109.00 -
×
 Nitrile Gloves Powder-Free, Blue, XS - Box of 150 (3 boxes/carton)
1 × $189.00
Nitrile Gloves Powder-Free, Blue, XS - Box of 150 (3 boxes/carton)
1 × $189.00 -
×
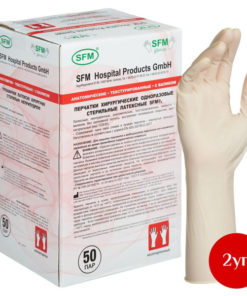 Sterile Latex Medical Gloves, Powder-Free, Size 8.0 (50 Pairs/Box, 2 Boxes)
1 × $159.00
Sterile Latex Medical Gloves, Powder-Free, Size 8.0 (50 Pairs/Box, 2 Boxes)
1 × $159.00 -
×
 Microfiber cloth Dora "For optics" 18*18 cm
1 × $9.00
Microfiber cloth Dora "For optics" 18*18 cm
1 × $9.00 -
×
 White Disposable Cat Mask
1 × $9.00
White Disposable Cat Mask
1 × $9.00
Subtotal: $769.00
 Free worldwide shipping on orders $99+
Free worldwide shipping on orders $99+
 US: 2–3 weeks,
US: 2–3 weeks,
 EU: 1–2 weeks,
EU: 1–2 weeks,
 Worldwide: 1–4 weeks
Worldwide: 1–4 weeks