-
×
 White Crochet Mesh Hat
1 × $9.00
White Crochet Mesh Hat
1 × $9.00 -
×
 Luxury Gray Goose Down Pillow with Memory Foam - Belpol GALAXY SEA 50x70x4
1 × $359.00
Luxury Gray Goose Down Pillow with Memory Foam - Belpol GALAXY SEA 50x70x4
1 × $359.00 -
×
 Queen Pillow, 60x60cm: Luxurious Comfort
1 × $99.00
Queen Pillow, 60x60cm: Luxurious Comfort
1 × $99.00 -
×
 VEYLE ERGO Memory Foam Pillow: Anatomical Support (39x59x10cm)
1 × $79.00
VEYLE ERGO Memory Foam Pillow: Anatomical Support (39x59x10cm)
1 × $79.00 -
×
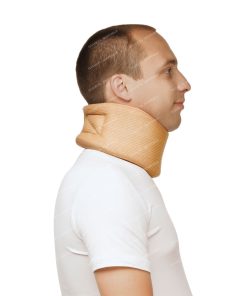 Bandage neck size 2
1 × $19.00
Bandage neck size 2
1 × $19.00 -
×
 Orthopedic insoles for children. art. 26E p.13 "Effect"
1 × $19.00
Orthopedic insoles for children. art. 26E p.13 "Effect"
1 × $19.00 -
×
 Olive Green Convertible Multi-Purpose Tote Bag SURT-01
1 × $109.00
Olive Green Convertible Multi-Purpose Tote Bag SURT-01
1 × $109.00 -
×
 Pine Extract Briquettes (Direct from Manufacturer)
1 × $19.00
Pine Extract Briquettes (Direct from Manufacturer)
1 × $19.00
Subtotal: $712.00
 Free worldwide shipping on orders $99+
Free worldwide shipping on orders $99+  US: temporary delays — postal services aligning new import rules,
US: temporary delays — postal services aligning new import rules,  EU: 1–2 weeks,
EU: 1–2 weeks,  Worldwide: 1–4 weeks
Worldwide: 1–4 weeks